Description
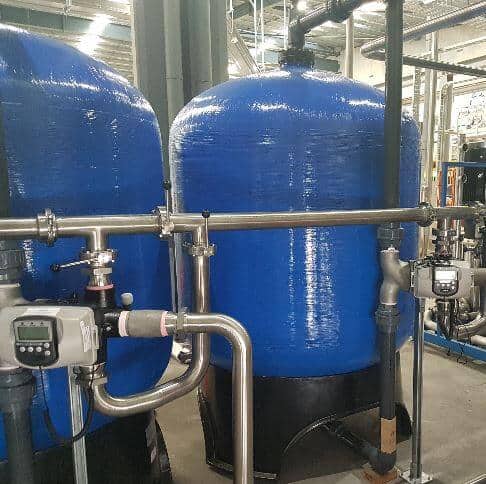
Description-Commercial Sediment Filter
Media Filter with Clack Automated Backwash Valve and Activated Glass Filtration Media .
Automated commercial sediment filter with mechanical or digital control valve for automated backwash and flush sequence. Includes gravel bed and loaded with activated glass media . Proven by independent testing, activated glass media has superior performance in comparison with quartz sand and other glass filter media
About Activated Glass Media
Activated Glass Filtration Media replaces traditional sand media in all filtration applications. It is manufactured from a specific glass type and processed to obtain the optimum particle size and shape, and then activated to increase the surface area by 300 times over crushed glass or sand. The high surface area is negatively charged (zeta potential) to electro-statically attract organics and small particles. It also has permanent metal oxide catalysts, creating a high redox potential, to make the activated glass media self-sterilising.
Main Benefits
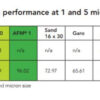
- Over 30% lower running costs vs sand
- Over 50% lower chlorine consumption and lower disinfection by-products vs sand
- Filtration down to several microns at 100% efficiency without filtration aids
- More than 4 times longer lifecycle than sand
- Specifically engineered product, targeted for an efficient removal of priority metal oxides and other target constitutes
- Guaranteed prevention of channeling & biological fouling on the AGFM surface

Recommended Media Grades and Arrangement from top to bottom (on a bottom plate), in Pressure Filters
| Grade | Size (mm) | Commercial Purification | High Purification | Ultra Purification |
| Grade 0 | 0.25 – 0.50 | N/A | 20% | 60% |
| Grade 1 | 0.4 – 1.0 | 70% | 50% | 20% |
| Grade 2 | 1 – 2 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
| Grade 3 | 2 – 6 | 15% | 15% | 10% |
Recommended applications
| Application Type | Removed by use of activated glass media |
| Drinking water | Iron, Manganese, Arsenic and other heavy metals Note ; Oxidation recommended |
| Municipal Wastewater | Phosphorous & Bacteria, BOD, COD & TOC Reduction |
| Industrial Process Water | Organic pollutants & oils, TSS, VSS & Particles < 1 micron |
| Industrial Wastewater | Colours and fine fibers, Residual mineral oils |
Product Details
Name | Activated Glass Filtration Media (AGFM) |
| Usage | Replacement for sand in all media filtration applications |
| Material | Green recycled glass, uniquely shaped particles with activated surface |
| Unique Features | Bio-resistant, self-sterilizing, sustainable, activated filtration media |
About Clack Valves
- Designed for residential, commercial and industrial use
- Clack control valves are state of the art automatic valves that cover a broad range of global applications
- Use with sizes up to 3″ and flow rates up to 250 GPM (56.8 m3/hr)
- The valves can service tanks up to 63″ inch diameter
- The cycles can be set for downflow or upflow regeneration, or simply service, backwash and rinse and are the easiest valves to service in the industry
- The valves come in different program versions and are controlled by solid state microprocessors with front panel settings and screen display
- They are simple to configure for use in multiple tank systems
- The valves come in different program versions and are controlled by solid state microprocessors with front panel settings and screen display
- The valves have a complete line of accessories including stainless steel flow meters, motorized alternating valves, no hard water bypass and system controllers
About Turbidity
Turbidity is a measure of water clarity how much the material suspended in water decreases the passage of light through the water. Suspended materials include soil particles (clay, silt, and sand), algae, plankton, microbes, and other substances. These materials are typically in the size range of 0.004 mm (clay) to 1.0 mm (sand). Turbidity can affect the colour of the water.
Higher turbidity increases water temperatures because suspended particles absorb more heat. This, in turn, reduces the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) because warm water holds less DO than cold. Higher turbidity also reduces the amount of light penetrating the water, which reduces photosynthesis and the production of DO. Suspended materials can clog fish gills, reducing resistance to disease in fish, lowering growth rates, and affecting egg and larval development. As the particles settle, they can blanket the stream bottom, especially in slower waters, and smother fish eggs and benthic macroinvertebrates. Sources of turbidity include:
- Soil erosion
- Waste discharge
- Urban runoff
- Eroding stream banks
- Large numbers of bottom feeders (such as carp), which stir up bottom sediments
- Excessive algal growth.

Measuring Turbidity
Turbidity can be measured using either an electronic turbidity meter or a turbidity tube. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages, as shown below. Turbidity is usually measured in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU) or Jackson turbidity units (JTLJ),
The two units are roughly equal.
Removing Turbidity with an automatic backwash filter.
Sediment (floating particulates, sand, clay, etc.) and turbidity (suspended solids that cause cloudiness) are common problems in a wide variety of water situations. Removal of these contaminates provides clearer, cleaner water that is more appealing to the eyes.
Backwashing sediment filters offer a distinct advantage over typical cartridge filter systems with significantly reduced maintenance requirements. Since the system automatically backwashes itself there are no filters to change, which not only cuts down on maintenance time but costs as well.