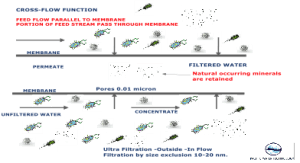
Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration can be used to meet very distinct liquid separations.
[Ultrafiltration]
Membrane Filtration Systems
Pacific Water Technology has teamed up with leading manufacturers of membrane systems to provide solutions for potable and wastewater treatment applications, as well as applications in the food and pharmaceutical industry.
The membrane technology market is witnessing significant growth due to increasing research and development and production in the pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical and life sciences industries. Thus, the rise in pharmaceutical production and the increasing number of membrane technology applications worldwide are driving the growth of membrane technology in water treatment, pharmaceutical, bio-pharmaceutical and life sciences industries.
Additionally, stringent regulations and the usage of single-use disposable techniques are playing a major role in the growth of the membrane technology market. The presence of various filtration techniques such as ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and microfiltration under membrane technology has increased its acceptance in pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical and life science industries for the separation and purification of components and biomolecules, over conventional techniques.
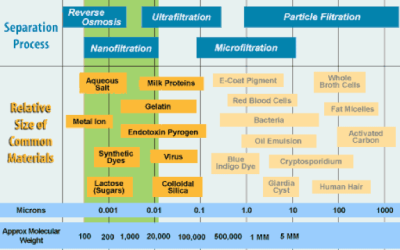
Ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, microfiltration and RO all have a specific place in the filtration application spectrum, which extends far beyond the water treatment industry.
Below is a comparison of how the different forms of membrane filtration have evolved into niche markets and potential applications. Ultrafiltration, for instance, has become a popular filtration technique in the bottled water industry for removing bacteria, macromolecules and most viruses without removing healthy minerals like calcium and magnesium. In many applications, ultrafiltration has replaced sand filters. Nanofiltration goes one step further and removes bivalent ions including the hardness of salts calcium and magnesium, hence softening the water.
RO FILTRATION
- Purification of surface water, groundwater and spring water to make drinking water and process water.
- Desalination of seawater and brackish water
- Dewatering process streams, concentrating/separating low-molecular-weight substances in solution, or cleaning wastewater.