| Ultrafiltration (UF) is a pressure-driven process that removes emulsified oils, metal hydroxides, colloids, emulsions, dispersed material, suspended solids, and other large molecular weight materials from water and other solutions. UF membranes are characterized by their molecular weight cut-off.
UF excels at the clarification of solutions containing suspended solids, bacteria, and high concentrations of macromolecules, including oil and water, fruit juice, milk and whey, electrocoat paints, pharmaceuticals, poly-vinyl alcohol and indigo, potable water, and tertiary wastewater.
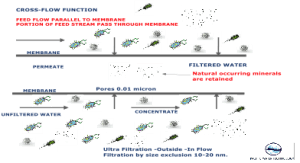
Ultrafiltration, like reverse osmosis, is a cross-flow separation process. Here liquid stream to be treated (feed) flows tangentially along the membrane surface, thereby producing two streams. The stream of liquid that comes through the membrane is called permeate. The type and amount of species left in the permeate will depend on the characteristics of the membrane, the operating conditions, and the quality of feed. The other liquid stream is called concentrate and gets progressively concentrated in those species removed by the membrane. In cross-flow separation, therefore, the membrane itself does not act as a collector of ions, molecules, or colloids but merely as a barrier to these species.
Conventional filters such as media filters or cartridge filters, on the other hand, only remove suspended solids by trapping these in the pores of the filter-media. These filters therefore act as depositories of suspended solids and have to be cleaned or replaced frequently. Conventional filters are used upstream from the membrane system to remove relatively large suspended solids and to let the membrane do the job of removing fine particles and dissolved solids. In ultrafiltration, for many applications, no prefilters are used and ultrafiltration modules concentrate all of the suspended and emulsified materials.
In high purity water systems, ultrafiltration is slowly replacing the traditional 0.2-micron cartridge filters. In Japan, practically all of the semiconductor industry follows this practice. An ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular-weight cutoff of 10,000 has a nominal pore size of 0.003 micron. When an ultrafiltration membrane is used instead of a 0.2-micron cartridge filter, particle removal efficiency is greatly improved. In addition, ultrafiltration membranes are not susceptible to the problem of bacteria growing through them, as is the case with 0.2-micron filters.
One of the most sophisticated uses of ultrafiltration lies in the application of membrane bioreactors (MBR) for wastewater. The ultrafiltration can operate in the normal way on a cross-flow by-pass system, or submerged in the bioreactor vessel by means of vacuum suction at low trans-membrane pressures.
The combination of activated sludge with membrane separation in the MBR results in efficiencies of footprint, effluent quality and residuals production that cannot be attained when these same processes are operated in sequence.
The primary advantages of low-pressure UF membrane processes compared with conventional clarification and disinfection (post chlorination) processes are:
- No need for chemicals (coagulants, flocculates, disinfectants, pH adjustment).
- Ideal for drinking and beverage water sterile filtration where the natural occurring minerals are retained.
- Provides more stable and less corrosive water in drinking water applications.
- Size-exclusion filtration as opposed to media depth filtration.
- Good and constant quality of the treated water in terms of particle and microbial removal.
- Process and plant compactness; and simple automation.
- Low fouling membrane modules
- Excellent filtration performance with high flux
- High chemical resistance and temperature tolerance for effective membrane cleaning
- Very fine nominal pore diameter (0.03 µm)
- High removal efficiency of bacteria and viruses
- Dead-end or concentrate bleed flow capabilities.
- Can be periodically back washed and air scoured to improve performance and extend operating life by removing the fouling layer
- Simple, vertical, modular design allows low cost, compact systems.
- UF Outside-In or Inside-Out Configuration allows for less plugging and higher solids loading, higher flow area and easier cleaning.
Typical applications are:
- Sterile filtration of drinking and beverage water
- Treatment of surface water
- Recovery of filter backflushing water
- Separation of oil/water emulsions
- Recovery of electrodeposition paint
- Removal of metal hydroxides in wastewater treatment
- Separation of biomass in biotechnology
- Wastewater treatment and re-use
- Membrane bioreactors
Pacific Water Technology can fabricate an ultrafiltration plant to suit your requirements for various applications including drinking water and wastewater applications.
Datasheets:
GIGAMEM_Polymem
_UKGIGAMEM-UF2555-S2F-VA
GIGAMEM-UF80G-S2F-VA
|













